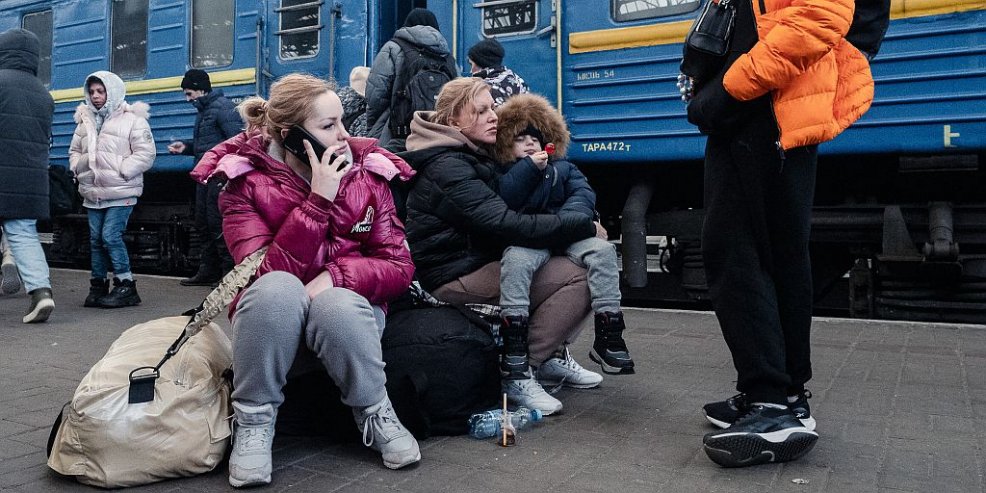
This article was first published by Liz Specht, associate director of science and technology at The Good Food Institute, at Statnews.com with title What does the coronavirus mean for the U.S. health care system? Some simple math offers alarming answers. Posting the Article here with her permission.
Much of the current discourse on — and dismissal of — the Covid-19 outbreak focuses on comparisons of the total case load and total deaths with those caused by seasonal influenza. But these comparisons can be deceiving, especially in the early stages of an exponential curve as a novel virus tears through an immunologically naïve population.
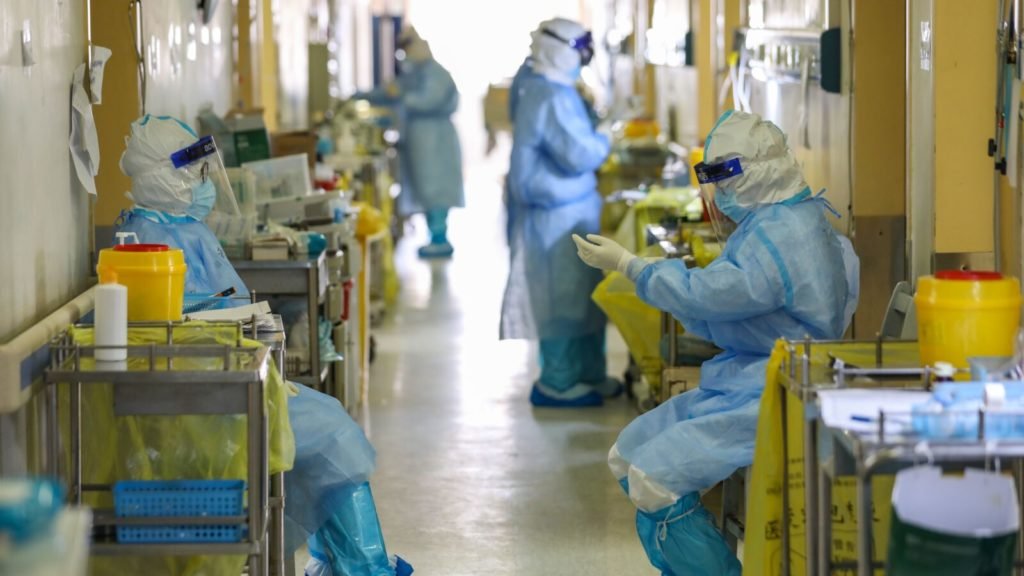

Perhaps more important is the disproportionate number of severe Covid-19 cases, many requiring hospitalization or weekslong ICU stays. What does an avalanche of uncharacteristically severe respiratory viral illness cases mean for our health care system? How much excess capacity currently exists, and how quickly could Covid-19 cases saturate and overwhelm the number of available hospital beds, face masks, and other resources?
This threat to the health care system as a whole poses the greatest challenge.
As I initially described in a Twitter thread, simple mathematics can derive rough estimates for how this might play out.
This exercise can inform our level of urgency and equip us to anticipate non-obvious, second-order effects, some of which can be mitigated with proper preparation.
As of March 8, about 500 cases of Covid-19 had been diagnosed in the U.S. Given the substantial underdiagnosis at present due to limitations in testing for the coronavirus, let’s say there are 2,000 current cases, a conservative starting bet.
We can expect a doubling of cases every six days, according to several epidemiological studies. Confirmed cases may appear to rise faster (or slower) in the short term as diagnostic capabilities are ramped up (or not), but this is how fast we can expect actual new cases to rise in the absence of substantial mitigation measures.
That means we are looking at about 1 million U.S. cases by the end of April; 2 million by May 7; 4 million by May 13; and so on.
As the health care system becomes saturated with cases, it will become increasingly difficult to detect, track, and contain new transmission chains. In the absence of extreme interventions like those implemented in China, this trend likely won’t slow significantly until hitting at least 1% of the population, or about 3.3 million Americans.
What does a case load of this size mean for health care system? That’s a big question, but just two facets — hospital beds and masks — can gauge how Covid-19 will affect resources.
The U.S. has about 2.8 hospital beds per 1,000 people (South Korea and Japan, two countries that have seemingly thwarted the exponential case growth trajectory, have more than 12 hospital beds per 1,000 people; even China has 4.3 per 1,000). With a population of 330 million, this is about 1 million hospital beds. At any given time, about 68% of them are occupied. That leaves about 300,000 beds available nationwide.
The majority of people with Covid-19 can be managed at home. But among 44,000 cases in China, about 15% required hospitalization and 5% ended up in critical care. In Italy, the statistics so far are even more dismal: More than half of infected individuals require hospitalization and about 10% need treatment in the ICU.
For this exercise, I’m conservatively assuming that only 10% of cases warrant hospitalization, in part because the U.S. population is younger than Italy’s, and has lower rates of smoking — which may compromise lung health and contribute to poorer prognosis — than both Italy and China. Yet the U.S. also has high rates of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes, which are also associated with the severity of Covid-19.
At a 10% hospitalization rate, all hospital beds in the U.S. will be filled by about May 10. And with many patients requiring weeks of care, turnover will slow to a crawl as beds fill with Covid-19 patients.
If I’m wrong by a factor of two regarding the fraction of severe cases, that only changes the timeline of bed saturation by six days (one doubling time) in either direction. If 20% of cases require hospitalization, we run out of beds by about May 4. If only 5% of cases require it, we can make it until about May 16, and a 2.5% rate gets us to May 22.
But this presumes there is no uptick in demand for beds from non-Covid-19 causes, a dubious presumption. As the health care system becomes increasingly burdened and prescription medication shortages kick in, people with chronic conditions that are normally well-managed may find themselves slipping into states of medical distress requiring hospitalization and even intensive care. For the sake of this exercise, though, let’s assume that all other causes of hospitalization remain constant.
Let me now turn to masks. The U.S. has a national stockpile of 12 million N95 masks and 30 million surgical masks for a health care workforce of about 18 million. As Covid-19 cases saturate nearly every state and county, virtually all health care workers will be expected to wear masks. If only 6 million of them are working on any given day (certainly an underestimate) they would burn through the national N95 stockpile in two days if each worker only got one mask per day, which is neither sanitary nor pragmatic.
It’s unlikely we’d be able to ramp up domestic production or importation of new masks to keep pace with this level of demand, especially since most countries will be simultaneously experiencing the same crises and shortages.
Shortages of these two resources — beds and masks — don’t stand in isolation but compound each other’s severity. Even with full personal protective equipment, health care workers are becoming infected while treating patients with Covid-19. As masks become a scarce resource, doctors and nurses will start dropping from the workforce for weeks at a time, leading to profound staffing shortages that further compound the challenges.
The same analysis applied to thousands of medical devices, supplies, and services — from complex equipment like ventilators or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation devices to hospital staples like saline drip bags — shows how these limitations compound one another while reducing the number of options available to clinicians.
Importantly — and I cannot stress this enough — even if some of the core assumptions I’m making, like the fraction of severe cases or the number of current cases, are off even by several-fold, it changes the overall timeline only by days or weeks.
Unwarranted panic does no one any good, but neither does ill-informed complacency. It’s inappropriate to assuage the public with misleading comparisons to the seasonal flu or by assuring people that there’s “only” a 2% fatality rate. The fraction of cases that are severe really sets Covid-19 apart from more familiar respiratory illnesses, compounded by the fact that it’s whipping through a population without natural immune protection at lightning speed.
Individuals and governments seem not to be fully grasping the magnitude and near-inevitability of the national and global systemic burden we’re facing. We’re witnessing the abject refusal of many countries to adequately respond or prepare. Even if the risk of death for healthy individuals is very low, it’s insensible to mock decisions like canceling events, closing workplaces, or stocking up on prescription medications as panicked overreaction. These measures are the bare minimum we should be doing to try to shift the peak — to slow the rise in cases so health care systems are less overwhelmed.
The doubling time will naturally start to slow once a sizable fraction of the population has been infected due to the emergence of herd immunity and a dwindling susceptible population. And yes, societal measures like closing schools, implementing work-from-home policies, and canceling events may start to slow the spread before reaching infection saturation.
But considering that the scenarios described earlier — overflowing hospitals, mask shortages, infected health care workers — manifest when infections reach a mere 1% of the U.S. population, these interventions can only marginally slow the rate at which our health care system becomes swamped. They are unlikely to prevent overload altogether, at least in the absence of exceedingly swift and austere measures.
Each passing day is a missed opportunity to mitigate the wave of severe cases that we know is coming, and the lack of widespread surveillance testing is simply unacceptable. The best time to act is already in the past. The second-best time is right now.
Liz Specht is the associate director of science and technology at The Good Food Institute.
Also check our previous articles
Coronavirus Disease 2019 COVID-19 A Pandemic: Is The World Ready?
Corona Virus Outbreak – Chinese Conspiracy Or Nature’s Curse?
Follow us at:-
Twitter Handle: @communique_news
Parler Handle: @newscommuniquecom
Subscribe our : YouTube Channel https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCnKJQ3gFsRVWpvdjnntQoAA
Like our Facebook Page https://m.facebook.com/News-Communiquecom-103788531007438/
1,120 total views