Indian Weapon Systems is the new series we are starting to let our readers know about strengths of India. At a time when China is flexing muscles for land grabbing in Union Territory of Ladakh and Pakistan is ready to jump in the two front war, India has to look at the readily available options in its inventory and the ones that can be quickly mass produced in its large Ordinance Factories or with Private Participation.
Today we bring to you Vidhwansak AMR Anti-Materiel Rifle
Specifications
Vidhwansak (Sanskrit:”The Destroyer”) is an Indian multi-caliber anti-materiel rifle (AMR) or large-caliber sniper rifle manufactured by Ordnance Factory Tiruchirappalli. It can be used in the anti-materiel role for destroying enemy bunkers, lightly armoured vehicles, radar systems, communication equipment, parked aircraft, fuel storage facilities, etc. It is also effective in long-range sniping, counter sniping and ordnance disposal roles.

Vidhwansak is a manually operated, rotating bolt-action rifle. The barrel along with the receiver recoil inside the chassis frame against a damping system. The rifle is fed from a detachable box magazine that is inserted from the left side. The rifle can be quickly disassembled and carried in two man-portable packs, each weighing about 12 to 15 kg. A muzzle brake is fitted on the end of the barrel which absorbs an estimated 50-60% of recoil. This is further supplemented by a buffered slide in the receiver.
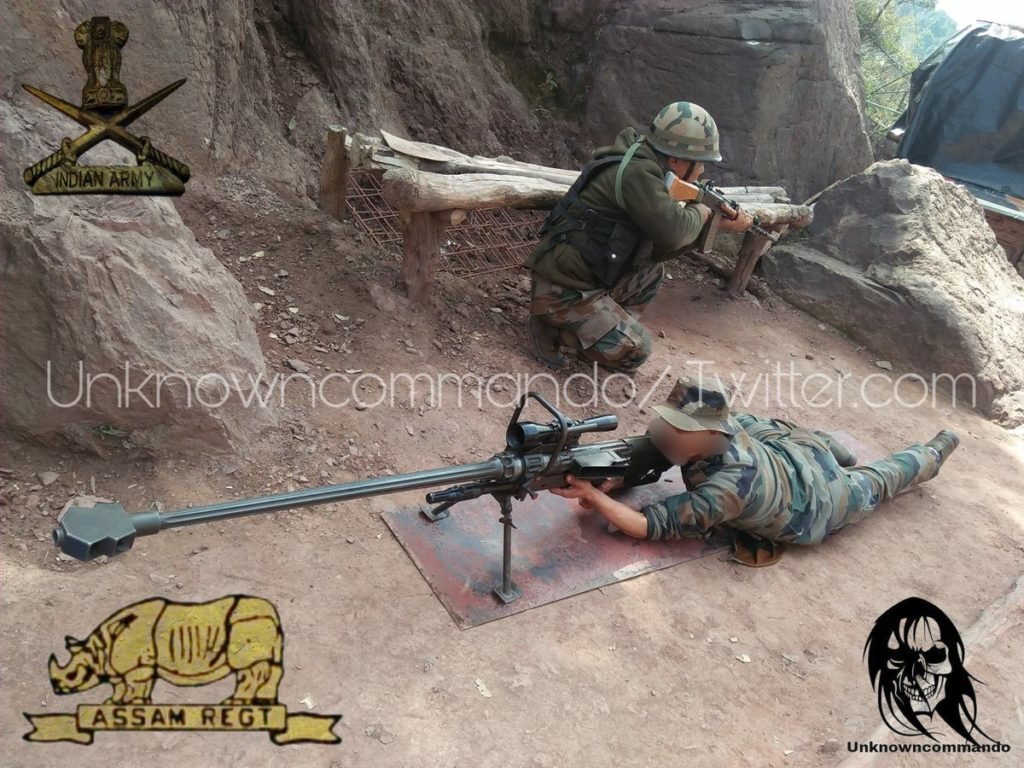

Vidhwansak is equipped with an 8X magnification, long-eye-relief telescopic sight with parallax adjustment. A 12X ballistic scope can also be attached. The rifle has an effective range of 1,800 m (1,300 m for the 20 mm version),while shots can be achieved even up to 2,000 m. The rifle is magazine fed, and reloaded through manual bolt action.Vidhwansak AMR is one of few firearms to support 3 calibers with quick interchangeability (without completely disassembling and reworking the weapon).

The Vidhwansak can be easily converted between the three calibers – 12.7 mm, 14.5 mm and 20 mm, by replacing the barrel, bolt, magazine and scope, which takes about 1 minute in the field, without the need for any specialized tools

An addition of Tonbo Imaging scope can increase its range considerably. Tonbo Imaging’s MarkO recognizes human targets at >2.5 kms and comes integrated with LRF and Met sensors for auto ballistic correction. Can be used in clip-on, standalone or handheld config.
Recommended Article : Chinese Aggression at Indian Border Fails – Situation Still Tense
Vidhwansak Anti-Material Guns with Indian Army
The Vidhwansak is an indigenous anti-material rifle design currently in limited service with the Indian Army. The large and heavy rifle system is intended as a complementary battlefield fixture to combat enemy light vehicles, structures, fortifications, ordnance disposal and counter-sniping. The rifle entered service in 2007 to fulfill an Indian Army need for such a weapon system. Exact number of rifles in operation are not known.
The Indian Army was, at first, in talks with the South African defense firm of Denel to deliver different types of weapon systems as being requested. One of the procurement requirements was for an anti-material rifle that was to be the Denel NTW-20 series system. However, it was revealed that the Denel firm was responsible for unlawful payments to the Indian government in order to secure the lucrative defense contracts and the firm was promptly banned from service with the Indian military as a result.
Recommended Article : The Armed Forces Of India : Unyielding – By Lt Gen PR Shankar (Retd)
This left the Indian Army with various military-oriented gaps to fill, chief among these still being the need for a proven anti-material weapon system. As such, local work on a solution began with the Ordnance Factory Tiruchirapalli (OFT) teaming with the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) of New Delhi to produce a suitable replacement of indigenous origin. The DRDO emerged in 1958 to manage the development of technology to be used by the Indian military.
Taking the South African NTW-20 as a starting point, development produced a working prototype by the end of 2005. Evaluation began in 2006 and completed with success, leading to the procurement contract for 100 Vidhwansak to be delivered to the Indian Border Security Force – India’s border patrol agency. Production of the Vidhwansak series formally began in February of 2007 and the weapon was officially delivered in October of 2008. Despite the limited procurement as of now, the Indian Army and other government defense groups have shown interest in the rifle system.
Unique to the Vidhwansak is the ability for the base weapon system to accept three different calibers with a few limited changes to her major components – the barrel and bolt. Additionally, the operator can mount an applicable optics system for the preferred caliber and must also supply the correct caliber ammunition magazine. The rifle can be made to fire cartridges in the form of 12.7mm, 14,5mm and 20mm calibers which makes the Vidhwansak a very flexible tactical weapon system.
Like other heavy rifles of this class, the Vidhwansak is a manually-actuated bolt-action rifle at her core. Regardless of the selected caliber of ammunition, the weapon feeds from a detachable box magazine inserted into the left side of the receiver. The receiver contains a buffered slide to contend with the violent recoil inherent in such weapons. Additionally, a muzzle brake is added to the barrel end to compensate for about half of the presented recoil during the firing action. The barrel and the receiver both recoil inside of the receiver frame. Design is such that the Vidhwansak can be broken down into two major components for travel by two designated personnel. Weight of the Vidhwansak is listed at a manageable 55lbs with a length of 1,700mm and a barrel length of 1,100mm. The Vidhwansak is typically issued with a crew of two operators to help facilitate the weapon needs. An 8×42 Power adjustable telescopic sight is issued as standard. Muzzle velocity is rated at 3,411 feet per second. Effective range is out to 1,962 yards with a maximum range out to 2,180 yards.
Recommended Article : China’s Strategic Myopia – By Lt Gen PR Shankar (Retd), India
Points to Ponder
Will Indian Government give Made in India a boost at the time of a looming two front war? How fast Indian Ordinance Factories can mass produce these Guns for a two front war? Would it be easy for Indian Government to get readily available Vidhwansak Rifles produced at large scale rather than going through the tender process with fresh tenders that may take years?
Twitter Handle: @newscomworld
Instagram Handle: @newscomworld
Parler Handle: @newscommuniquecom
Subscribe our : YouTube Channel https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCnKJQ3gFsRVWpvdjnntQoAA
Like our Facebook Page https://m.facebook.com/News-Communiquecom-103788531007438/
3,972 total views